New MITM6 and NTLM Relay Attack: How Attackers Can Elevate Privileges and Compromise Entire Domains
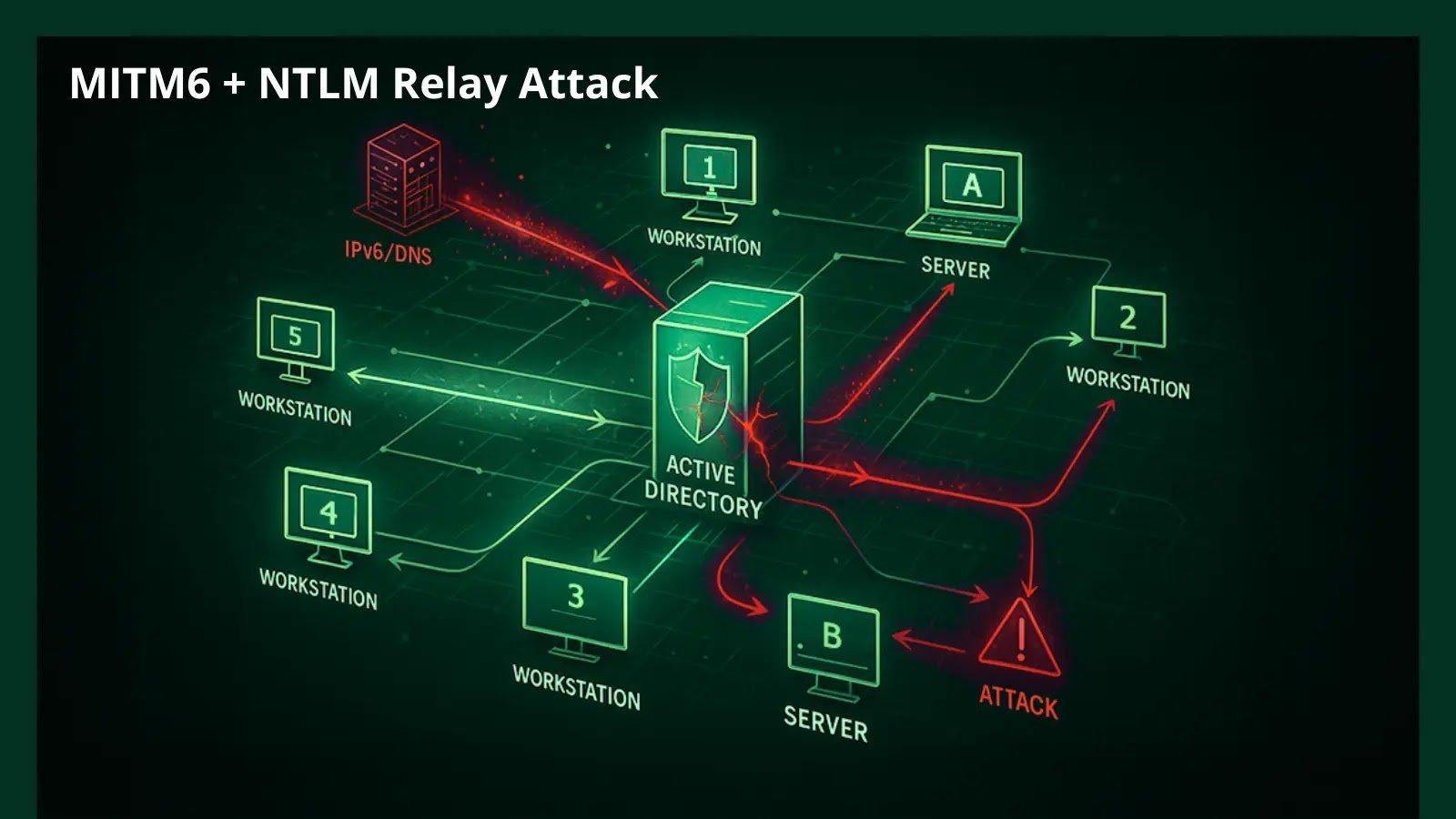
A sophisticated attack chain combines MITM6 with NTLM relay techniques to achieve full Active Directory domain compromise. This attack exploits Windows’ default IPv6 auto-configuration behaviour, enabling attackers to escalate from network access to Domain Admin privileges within minutes. Key takeaways include the abuse of Windows IPv6 auto-configuration and Active Directory’s 10-machine account quota for domain compromise. The attack employs mitm6 and ntlmrelayx to create malicious accounts with Resource-Based Constrained Delegation (RBCD), facilitating rapid elevation to Domain Admin status. To mitigate these risks, organisations should disable IPv6, set the ms-DS-MachineAccountQuota to 0, enable signing, and deploy DHCPv6 Guard. This technique poses significant threats to organisations operating standard Windows environments, as it leverages built-in protocols without the need for malware or zero-day exploits.
The MITM6 attack specifically targets a fundamental Windows behaviour: automatic DHCPv6 requests sent when systems boot or connect to networks. Even in organisations not actively using IPv6, Windows machines prioritise IPv6 configuration over IPv4, creating an exploitable attack surface. Attackers deploy the mitm6 tool to act as a rogue DHCPv6 server, responding to these requests and assigning malicious DNS server addresses to victim machines. The attack chain continues with ntlmrelayx from the Impacket toolkit, which intercepts NTLM authentication attempts through Web Proxy Auto-Discovery Protocol (WPAD) spoofing. This allows attackers to create malicious computer accounts and configure RBCD, leveraging Active Directory’s default ms-DS-MachineAccountQuota setting. Once successful, attackers can extract NTLM hashes and conduct lateral movement, leading to severe consequences such as full domain compromise, credential theft, service disruption, and potential data exfiltration.
Categories: Cybersecurity Threats, Active Directory Exploits, Mitigation Strategies
Tags: MITM6, NTLM Relay, Active Directory, IPv6, DHCPv6, RBCD, Domain Admin, Credential Theft, Network Compromise, Lateral Movement