GPUGate Malware Exploits Google Ads and GitHub to Distribute Sophisticated Malware Payloads
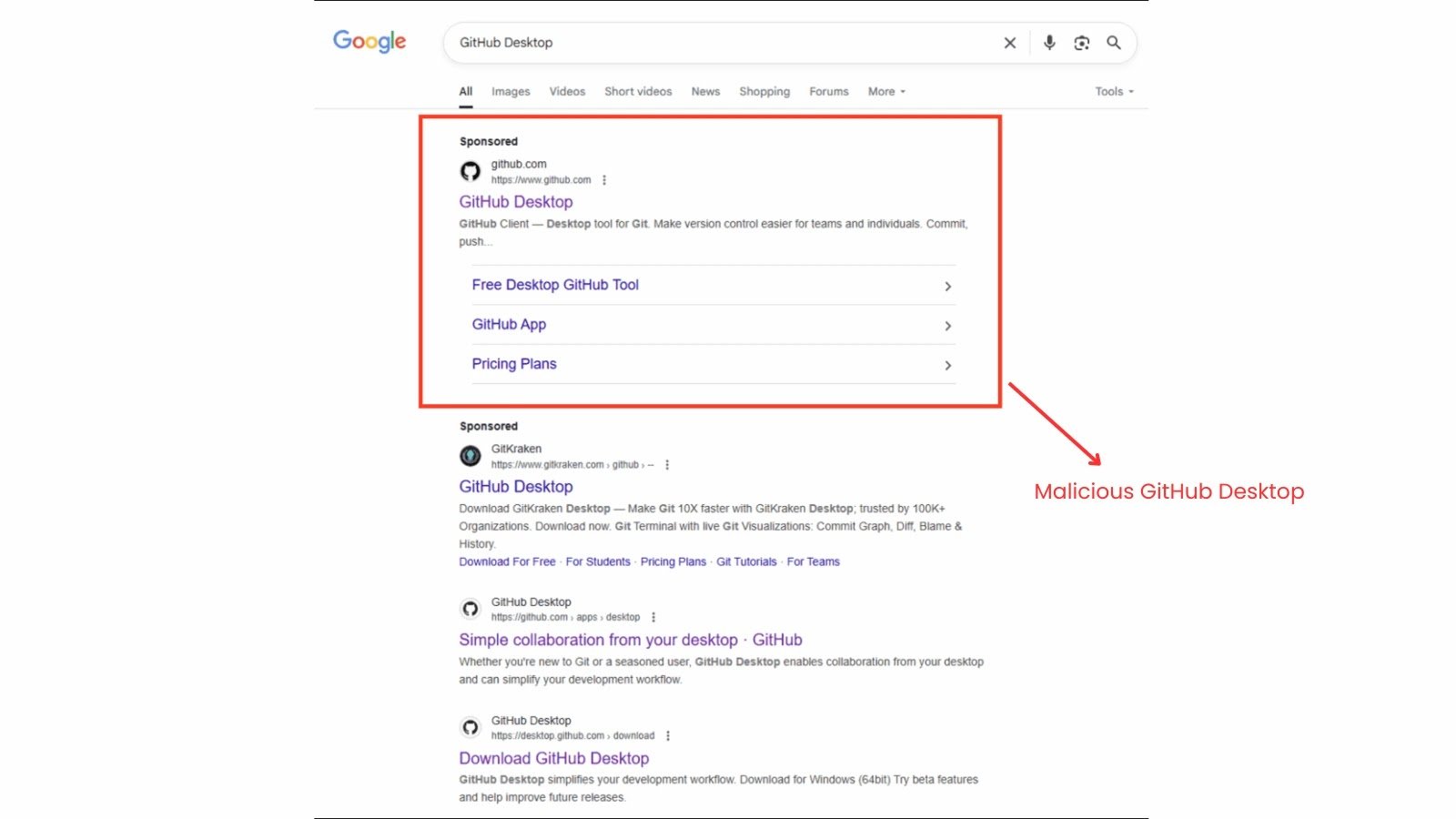
A sophisticated malware campaign, known as “GPUGate,” exploits Google Ads and GitHub’s repository structure to deceive users into downloading malicious software. According to the Arctic Wolf Cybersecurity Operations Center, this attack chain employs a novel technique that leverages a computer’s Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) to evade security analysis. The campaign, attributed to a Russian-speaking threat actor, primarily targets IT professionals in Western Europe. The attack initiates with malicious advertising, where attackers place sponsored ads at the top of Google search results for terms like “GitHub Desktop.” These ads redirect users to a seemingly legitimate GitHub page, which actually leads to a manipulated “commit” page within a repository. This page retains the repository’s name and metadata but contains altered download links that direct users to an attacker-controlled domain, exploiting the trust users place in both Google and GitHub.
What distinguishes GPUGate is its unique evasion method. The initial installer is a large 128 MB file, specifically designed to bypass security sandboxes that often impose file size limits. Its most innovative feature is a GPU-gated decryption routine, which only decrypts the malicious payload if it detects a real, physical GPU with a device name longer than ten characters. This tactic effectively thwarts analysis, as virtual machines and sandboxes used by security researchers typically have generic, short GPU names or lack a GPU altogether, leaving the payload encrypted and inert on such systems. The primary objective of this campaign is to gain initial access to organisational networks for malicious activities, including credential theft, data exfiltration, and ransomware deployment. By targeting developers and IT workers—individuals likely to seek tools like GitHub Desktop—the attackers aim for victims with elevated network privileges. Once executed, the malware employs a PowerShell script to gain administrative rights, create scheduled tasks for persistence, and add exclusions to Windows Defender to avoid detection. Active since at least December 2024, this campaign represents an evolving and significant threat.
Categories: Malware Campaigns, Cybersecurity Threats, Social Engineering Techniques
Tags: GPUGate, Malware, Google Ads, GitHub, Threat Actor, IT Professionals, Credential Theft, Data Exfiltration, Ransomware, Evasion Technique